Since December 3rd Let’s Encrypt is in Public Beta. I’m testing and using Let’s Encrypt for my virtual services in my homelab. Let’s Encrypt creates certificates with a lifetime of 90 days. Some of you will say: UH! that’s not pretty long.
I will show you my way to automate the process by the example of my KEMP Loadbalancer.
The check and renew process could be used for many solutions, not only to deploy to KEMP VLM.
Prerequirements:
- KEMP LoadBalancer ( HTTP and HTTPS Service. Last with Lets Encrypt Certificate)
- Certificate name www.YOURDOMAIN.com
- Ubuntu Server
- Apache Server for DNS verification on Port 80
- Installed Let’s Encrypt
- cli.ini created in /etc/letsencrypt folder (in the LE_cert_check_create.zip)
- created /certs directory
- Download scripts and ini from here (LE_cert_check_create.zip)
- save the two .sh scripts in /usr/local/sbin
- save the cli.ini in your letsencrypt config folder (e.g. /etc/letsencrypt)
- after your configuration and testing is done, save the cert_check file in /etc/cron.daily. So the script checks the certificate daily and renew it like you want.
For verification I use the webroot method. The LoadBalancer routes traffic for the .well-known/acme-challenge folder to the Ubuntu Server. This folder is used by Lets Encrypt to put checkfiles on it and verify it via http from the Let’s Encrypt Server.
I save the certificates to the folder /certs. So all certificates created by Lets Encrypt are not changed.
The scripts
I’ve created two scripts to 1st) check the lifetime of the existing certificate and renew it if necessary and 2nd) replace the certificate on KEMP VLM.
The scripts are linked at the end of the post.
- cert_check_create.sh
Check lifetime of existing certificate and renew it if the lifetime is shorter than 30 days (2592000 seconds)
At the end of the script I call my second script to replace the certificate on KEMP VLM.
This part could be easily changed to a different deployment method to another LoadBalancer or Webserver solution.
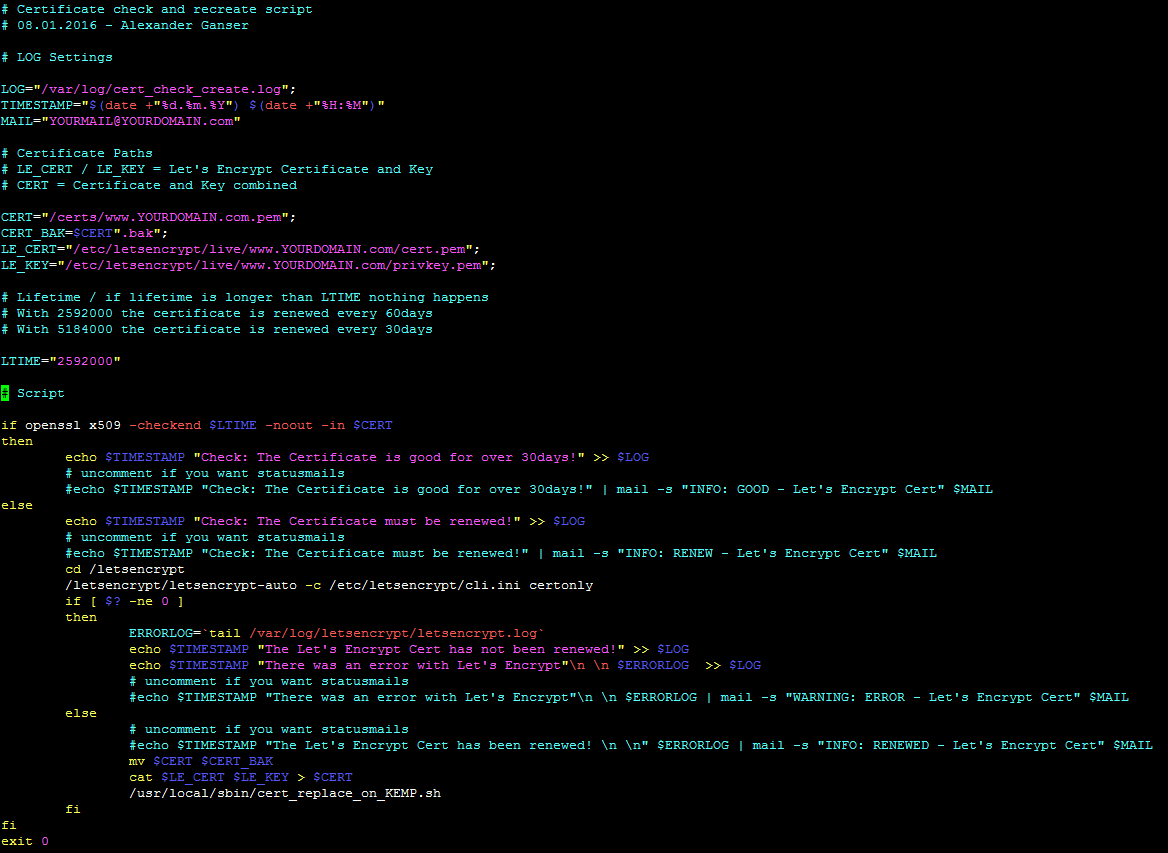
/usr/local/sbin/cert_check_create.sh
- A much smaller script :) To replace a certificate on KEMP VLM you can use the RESTFUL API. With curl the certificate is transfered to the VLM and after that it replaces the old one via addcert command with replace=1
![]()
/usr/local/sbin/cert_check_replace_on_KEMP.sh
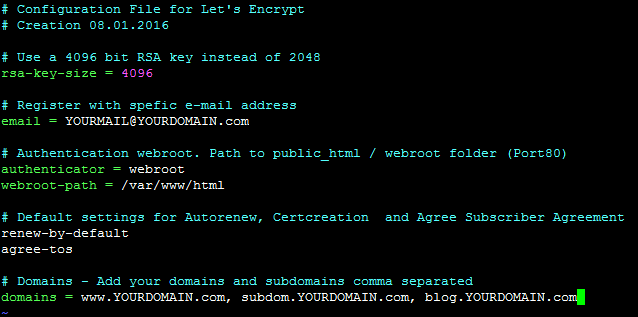
- /etc/letsencrypt/cli.ini
In the cli.ini you could set all options and domains which the certificate should contain.
Related documents:








Hi,
#!/bin/sh is missing from the scripts (however there is a small file containing only this)
line endings are CRLF causing problems.
Why CERT = Certificate and Key combined ?
Now I understand it: “Why CERT = Certificate and Key combined ?”
Because it’s easier to upload to KEMP this way